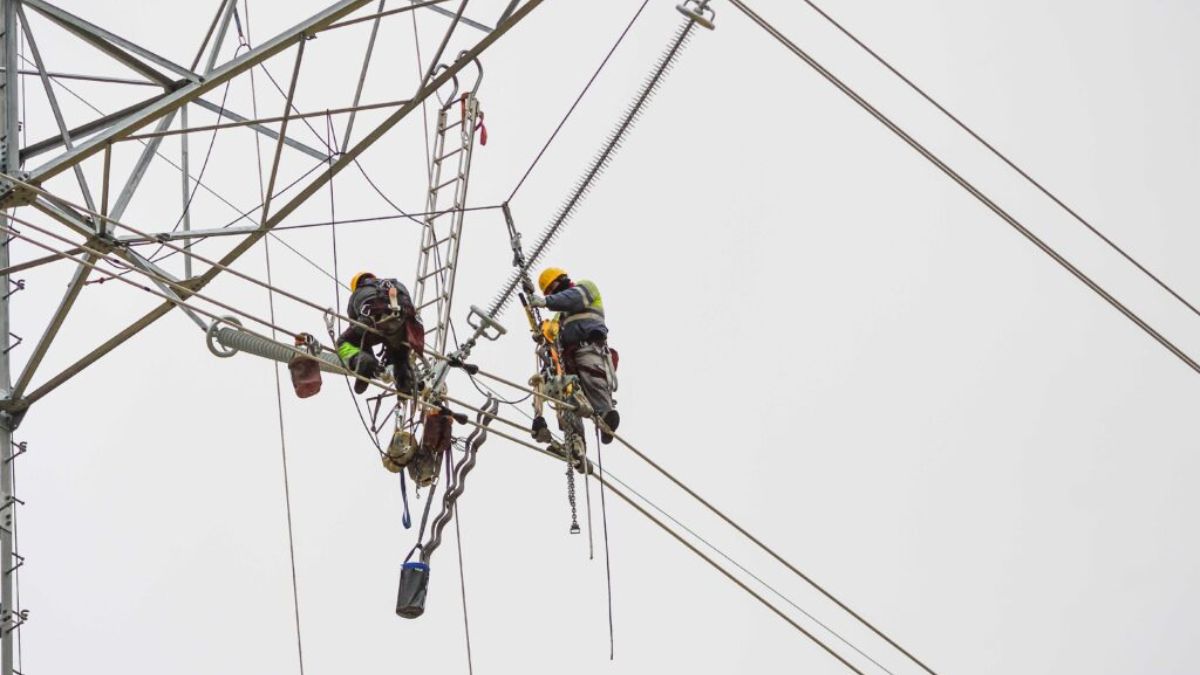
Pipelines serve as essential conduits for transporting oil, gas, and other critical materials across countries and continents. These intricate networks play a pivotal role in sustaining economies by ensuring that resources reach their destinations safely and efficiently. However, the integrity of these infrastructures heavily relies on consistent and thorough maintenance practices. Regular pipeline maintenance is not only crucial for operational safety and efficiency but also for minimizing environmental risks and extending the infrastructure’s lifespan. An integral component of this process is the utilization of pipeline pigs, which are instrumental in both cleaning and inspecting pipelines to uphold optimal performance standards.
This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of pipeline maintenance, shedding light on its importance and methods, the environmental impacts, the cost-benefit analysis, and future trends. We aim to furnish you with a deeper understanding of the significance and scope of pipeline maintenance, equipping you with insights for making informed decisions in a rapidly evolving industry.
Introduction to Pipeline Maintenance
Pipelines are essential lifelines in the global infrastructure landscape, responsible for the efficient and safe transportation of vital resources such as oil and natural gas. As these resources remain fundamental to powering industries and homes, the reliability and uninterrupted operation of pipelines are paramount. Optimal pipeline performance is achieved through regular maintenance schedules that address wear and tear, potential leaks, and any structural weaknesses. Ensuring that pipelines are well-maintained not only minimizes operational risks but also extends the life of the infrastructure. This proactive strategy plays a vital role in preemptively addressing issues that could potentially lead to costly repairs or catastrophic failures.
Importance of Scheduled Maintenance
Scheduled maintenance is a cornerstone in pipeline management, aiming to uphold the safety and efficiency of the entire network. It involves systematic inspections, cleanings, and repairs that prevent minor issues from escalating into emergencies. For instance, the infamous Bellingham, Washington incident in 1999, where a gas pipeline rupture led to tragic outcomes, underscores the dire consequences of neglecting maintenance. This unfortunate event highlighted how critical regular inspections and maintenance schedules are in preventing hazardous spills and ensuring community safety. Through scheduled interventions, pipeline operators can avoid such disasters, safeguard the environment, and maintain public trust in their operations.
Methods Used in Pipeline Maintenance
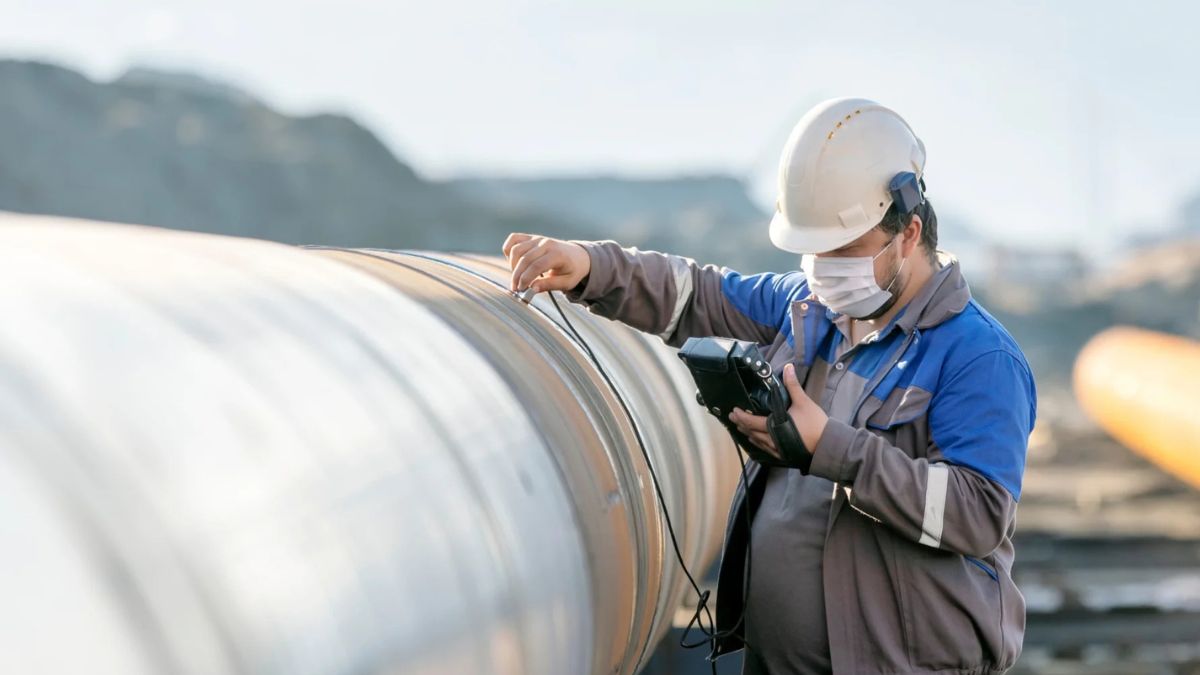
Pipeline maintenance is a sophisticated affair that involves several methods tailored to detect and rectify potential faults. A popular technique is hydrostatic testing, which helps identify leaks by filling pipelines with water and pressurizing them to levels beyond their operational limits. This method ensures that any weaknesses in the pipeline’s structure are promptly detected and addressed. Another cutting-edge practice involves inline inspections using sophisticated devices known as ‘smart pigs.’ These intelligent tools navigate through pipelines, collecting vital data that highlights any anomalies or defects requiring attention.
Technologies in Pipeline Monitoring
The advent of technology has revolutionized how pipelines are monitored and maintained. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and top-grade sensors now offer aerial perspectives, allowing operators to inspect extensive pipeline networks without setting foot on the ground. This approach enhances efficiency and enables timely identification of issues, particularly in remote or inaccessible locations, thus streamlining the maintenance process and reducing operational disruptions.
Environmental Impact of Pipeline Maintenance
The environmental benefits associated with regular pipeline maintenance are substantial. By preventing leaks and spills, optimal maintenance practices significantly reduce the environmental footprint of pipeline operations. Timely interventions ensure that pipelines function at peak efficiency, decreasing the likelihood of accidental discharges that could harm ecosystems and wildlife. Such proactive maintenance measures are integral to sustainable operations that align with environmental conservation efforts.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Regular Maintenance
The financial implications of pipeline maintenance are often perceived as burdensome; however, they pale in comparison to the potential costs of pipeline failures. Regular maintenance effectively preempts large-scale disasters, substantially lowering the need for emergency interventions that are both costly and labor-intensive. Data from Pipeline Safety Statistics illustrate the economic advantages of preventive maintenance, revealing that the expenses incurred in routine upkeep are significantly outweighed by the savings accrued from averting catastrophic failures.
Future Trends in Pipeline Maintenance
The future of pipeline maintenance is rife with potential, particularly as technological advancements continue to reshape the industry. The integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning heralds a new era of predictive maintenance. Leveraging AI-driven insights, operators can anticipate issues before they materialize, facilitating more efficient and cost-effective maintenance routines. According to the Future of Energy Infrastructure, these technologies are set to revolutionize pipeline management, paving the way for smarter, safer, and more sustainable operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, regular pipeline maintenance is indispensable for safeguarding the safety, efficiency, and sustainability of pipeline networks. It is an investment that pays dividends in the form of operational safety, environmental protection, and cost savings. By remaining committed to embracing cutting-edge technologies and methodologies, the industry can look forward to a future characterized by reliable and sustainable pipeline operations, ensuring that these vital infrastructures continue to support global needs effectively.